Clasificación de cáncer cervical usando redes neuronales convolucionales, transferencia de aprendizaje y aumento de datos
Cervical cancer classification using convolutional neural networks, transfer learning and data augmentation
Barra lateral del artículo
Términos de la licencia (VER)

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-SinDerivadas 4.0.
Declaración del copyright
Los autores ceden en exclusiva a la Universidad EIA, con facultad de cesión a terceros, todos los derechos de explotación que deriven de los trabajos que sean aceptados para su publicación en la Revista EIA, así como en cualquier producto derivados de la misma y, en particular, los de reproducción, distribución, comunicación pública (incluida la puesta a disposición interactiva) y transformación (incluidas la adaptación, la modificación y, en su caso, la traducción), para todas las modalidades de explotación (a título enunciativo y no limitativo: en formato papel, electrónico, on-line, soporte informático o audiovisual, así como en cualquier otro formato, incluso con finalidad promocional o publicitaria y/o para la realización de productos derivados), para un ámbito territorial mundial y para toda la duración legal de los derechos prevista en el vigente texto difundido de la Ley de Propiedad Intelectual. Esta cesión la realizarán los autores sin derecho a ningún tipo de remuneración o indemnización.
La autorización conferida a la Revista EIA estará vigente a partir de la fecha en que se incluye en el volumen y número respectivo en el Sistema Open Journal Systems de la Revista EIA, así como en las diferentes bases e índices de datos en que se encuentra indexada la publicación.
Todos los contenidos de la Revista EIA, están publicados bajo la Licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-NoDerivativa 4.0 Internacional
Licencia
![]()
Esta obra está bajo una Licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-NoDerivativa 4.0 Internacional
Contenido principal del artículo
Resumen
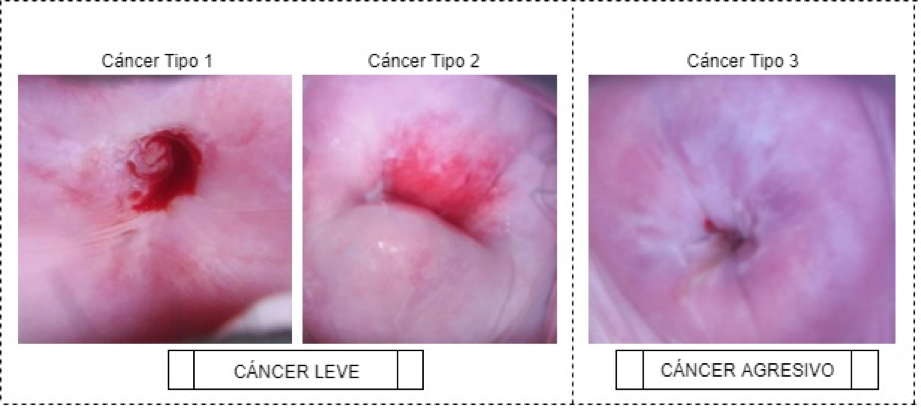
El cáncer cervical se forma en las células que revisten el cuello uterino y la parte inferior del útero. Debido a razones de costo y baja oferta de servicios destinados a la detección de este tipo de cáncer, muchas mujeres no tienen acceso a un diagnóstico pronto y preciso, ocasionando un inicio tardío del tratamiento. Para dar solución a este problema se implementó una metodología que clasifica de manera automática el tipo de cáncer cervical, entre leve (Tipo 1 y 2) y agresivo (Tipo 3), utilizando técnicas de procesamiento digital de imágenes y aprendizaje profundo. Se trabajó en la construcción de un modelo computacional con base en redes neuronales convolucionales, transferencia de aprendizaje y aumento de datos, obteniendo precisiones de clasificación de hasta 97,35% sobre los datos de validación, asegurando la confiabilidad de los resultados. Con este trabajo se demostró que el diseño propuesto puede ser usado como un complemento para mejorar la eficiencia de las herramientas del diagnóstico asistido del cáncer.
Descargas
Detalles del artículo
Reinel Tabares Soto, Universidad Autónoma de Manizales
Docente e investigador de la Universidad Autonóma de ManizalesReferencias (VER)
McGuire S. World cancer report 2014. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization, international agency for research on cancer, WHO Press, 2015. Advances in Nutrition: An International Review Journal, 7, 418-419, 2016.
Akshaya R., Manie R., Monisha B., Ranichadra V. Convolutional Neural Networks Aiding Colposcopy Image Classification. International Journal of Trend in Research and development, 5, 270-274, 2018.
Almonte M., Sánchez G.I., Jerónimo J., Ferreción C., Lazcano E., Herrera R. Nuevos Paradigmas en la Prevención y Control de Cáncer de Cuello Uterino en América Latina. Salud Pública de México, 52, No 6, 2010.
Lorena M., Villate S., Jiménez D., Conduct in regard to the papanicolaou test: The voice of the patients in face of abnormal growth in the cervix, Revista Colombiana de Enfermería, Vol. 18, páginas 1-13, 2019
Kaur N., Panagrahi N., Mittal A. Automated Cervical Cancer Screening Using Transfer Learning. International Journal Of Advanced Research in Science and Engineering, 6, 2110-2119, 2017.
Intel & MobileODT, Cervical Cancer Screening, 2017, [Online]. Available: https://www.kaggle.com/c/intel-mobileodt-cervical-cancer-screening/data
Simonyan K., Zisserman A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large Scale Image Recognition. Published as a conference paper at ICLR 2015. San Diego, California, Estados Unidos, abril, 2015.
Park Chansung, Transfer Learning in Tensorflow (VGG19 on CIFAR-10): Part 1, 2018, 10 Octubre 2019, [Online]. Available: https://towardsdatascience.com/transfer-learning-in-tensorflow-9e4f7eae3bb4
Stanford University, Princeton University, ImageNet, 2016, 10 Octubre 2019, [Online]. Available: http://www.image-net.org/
Zhang XQ, Zhao S-G, Cervical image classification based on image segmentation preprocessing and a CapsNet network model, Wiley, páginas 19-28, 2019 , [Online]. Available: https://doi.org/10.1002/ima.22291
Fernandes K., Cardoso J., Fernandes J., Automated Methods for the Decision Support of Cervical Cancer Screening Using Digital Colposcopies, IEEE Xplore, Vol. 6, páginas 33910-33927, 2018, [Online]. Available: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8362613
Vasudha, Mittal A., Juneja M., Cervix Cancer Classification using Colposcopy Images by Deep Learning Method, IJETSR, Vol. 5, páginas 426-432, 2018, [Online]. Available: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/f099/0cd17037129f7a55fcdf279ea6e9d613e8fe.pdf
Caraiman S., Vasile I., Histogram-based segmentation of quantum images, ELSEVIER, Vol. 529, páginas 46-60, 2014, [Online]. Available: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304397513005835
Adrian Rosebrock, pyimagesearch, Keras ImageDataGenerator and Data Augmentation(Julio 8, 2019), consultado por última vez el 10 de octubre del 2019 en: https://www.pyimagesearch.com/2019/07/08/keras-imagedatagenerator-and-data-augmentation/?utm_source=facebook&utm_medium=ad-08-07-2019&utm_campaign=8+July+2019+BP+-+Traffic&utm_content=Default+name+-+Traffic&fbid_campaign=6116019415846&fbid_adset=6116019416246&utm_adset=1+July+2019+BP+-+All+Visitors+90+Days+-+Worldwide+-+18%2B&fbid_ad=6116019417246
Mikolajczyk A. Grochowski M, Data augmentation for improving deep learning in image classification problem, IEEE Xplore, Poland, 2018, 21 Junio 2018, [Online]. Available: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8388338
Intel & MobileODT, Cervical Cancer Screening, 2017, [Online]. Available: https://www.kaggle.com/c/intel-mobileodt-cervical-cancer-screening
Tiago S. Nazar´e, Gabriel B. Paranhos da Costa, Welinton A. Contato, and Moacir Ponti, Deep Convolutional Neural Networks and Noisy Images, ResearchGate, paginas 416-424, 2018, [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/322915518_Deep_Convolutional_Neural_Networks_and_Noisy_Images
Nawal M. Nour, Cervical Cancer: A Preventable Death, Obstet Gynecol, Vol. 2, páginas 240-244, 2009, [Online]. Available: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2812875/
Ayan E, H. Muray Ü, Data augmentation importance for classification of skin lesions via deep learning, IEEE Xplore, páginas 1-5, 2019, [Online]. Available: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8391469/citations?tabFilter=papers#citations
Keras Documentation, Keras, [Online]. Available: https://keras.io/why-use-keras/
. TensorFlow Core r1.14, Tensorflow, [Online]. Available: https://www.tensorflow.org/versions/r1.14/api_docs/python/tf
Krizhevsky A., Sutskever I., Hinton G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In NIPS, 2012.
Abien Fred M. Agarap, Cornell University, Deep Learning using Rectified Linear Units (ReLU), 2019, 7 febrero 2019, [Online]. Available: https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.08375
Sridhar Narayan, The generalized sigmoid activation function: Competitive supervised learning, ScienceDirect, Vol. 99, páginas 69-82, 1997, [Online]. Available: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0020025596002009
Daniel Godoy, Towards Data Science, Understanding binary cross-entropy / log loss: a visual explanation, 2018, 10 octubre 2019, [Online]. Available: https://towardsdatascience.com/understanding-binary-cross-entropy-log-loss-a-visual-explanation-a3ac6025181a
Zhang S., Choromanska A., and LeCun Y.. Deep learning with Elastic Averaging SGD. Neural Information Processing Systems Conference (NIPS 2015), Vol. 28, páginas 1–24, 2015, [Online]. Available: https://papers.nips.cc/paper/5761-deep-learning-with-elastic-averaging-sgd
Piotr Skalski, Towards Data Science, Preventing Deep Neural Network from Overfitting, 2018, 10 Octubre 2019, [Online]. Available: https://towardsdatascience.com/preventing-deep-neural-network-from-overfitting-953458db800a
Srivastava N., Hinton G., Krizhevsky A., Sutskever I., Salakhutdinov R., Dropout: A Simple Way to Prevent Neural Networks from Overfitting, Journal of Machine Learning Research, Vol. 15, páginas. 1929-1958, 2014, [Online]. Available: http://jmlr.org/papers/v15/srivastava14a.html
Artículos similares
- Fernando Maureira Cid, Hernán Díaz Muñoz, Marcelo Hadweh Briceño, Análisis no-lineal de la onda gamma del EEG en una prueba de atención e inhibición , Revista EIA: Vol. 20 Núm. 40 (2023): Tabla de contenido Revista EIA No. 40
- Fernando Maureira Cid, Marcelo Hadweh Briceño, Actividad eléctrica no lineal de las ondas beta cerebrales durante una prueba de atención alternante e inhibición de la interferencia , Revista EIA: Vol. 19 Núm. 38 (2022): Tabla de contenido Revista EIA No. 38
- Fernando Maureira Cid, Hernán Díaz-Muñoz, Actividad eléctrica no lineal de las ondas beta cerebrales durante una prueba de atención sostenida , Revista EIA: Vol. 18 Núm. 36 (2021):
También puede {advancedSearchLink} para este artículo.

 PDF
PDF
 FLIP
FLIP