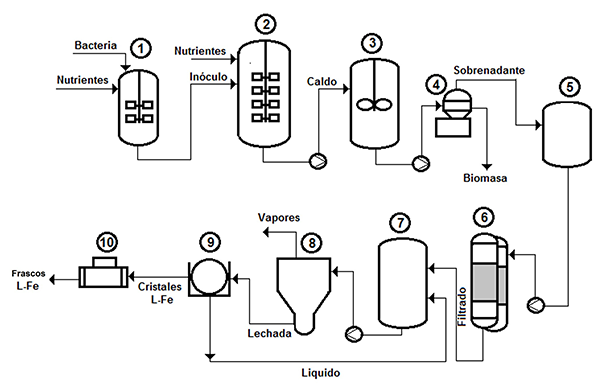
Simulación del proceso de producción de L-fenilalanina por la ruta fermentativa utilizando el simulador SuperPro Designer®
Simulation of the L-phenylalanine production process by the fermentative route using SuperPro Designer® simulator
Barra lateral del artículo
Términos de la licencia (VER)

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-SinDerivadas 4.0.
Declaración del copyright
Los autores ceden en exclusiva a la Universidad EIA, con facultad de cesión a terceros, todos los derechos de explotación que deriven de los trabajos que sean aceptados para su publicación en la Revista EIA, así como en cualquier producto derivados de la misma y, en particular, los de reproducción, distribución, comunicación pública (incluida la puesta a disposición interactiva) y transformación (incluidas la adaptación, la modificación y, en su caso, la traducción), para todas las modalidades de explotación (a título enunciativo y no limitativo: en formato papel, electrónico, on-line, soporte informático o audiovisual, así como en cualquier otro formato, incluso con finalidad promocional o publicitaria y/o para la realización de productos derivados), para un ámbito territorial mundial y para toda la duración legal de los derechos prevista en el vigente texto difundido de la Ley de Propiedad Intelectual. Esta cesión la realizarán los autores sin derecho a ningún tipo de remuneración o indemnización.
La autorización conferida a la Revista EIA estará vigente a partir de la fecha en que se incluye en el volumen y número respectivo en el Sistema Open Journal Systems de la Revista EIA, así como en las diferentes bases e índices de datos en que se encuentra indexada la publicación.
Todos los contenidos de la Revista EIA, están publicados bajo la Licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-NoDerivativa 4.0 Internacional
Licencia
![]()
Esta obra está bajo una Licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-NoDerivativa 4.0 Internacional
Contenido principal del artículo
Resumen
Descargas
Detalles del artículo
Amaury Perez Sanchez, Universidad de Camaguey
Departamento de Ingenieria Quimica, Profesor Instructor, Especialista PrincipalReferencias (VER)
Aguiar, A. C. d.; Osorio-Tobón, J. F.; Silva, L. P. S.; Barbero, G. F.; Martínez, J. (2018). Economic analysis of oleoresin production from malagueta peppers (Capsicum frutescens) by supercritical fluid extraction. The Journal of Supercritical Fluids, 133, pp. 86-93. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.supflu. 2017.09.031.
Auli, N. A.; Sakinah, M.; Bakri, A. M. M. A.; Kamarudin, H.; Norazian, M. N. (2013). Simulation Of Xylitol Production: A Review. Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 7(5), pp. 366-372.
Baca, G. (2010). Evaluación de proyectos, 6ta ed., México D.F., McGraw-Hill/Interamericana Editores, S.A. de C.V, pp. 56-94.
Báez-Viveros, J. L.; Flores, N., Juárez, K.; Castillo-España, P.; Bolivar, F.; Gosset, G. (2007). Metabolic transcription analysis of engineered Escherichia coli strains that overproduce L-phenylalanine. Microbial Cell Factories, 6(1), pp. 1-20. https://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-6-30.
BIOTOL. (1997). Biotechnological Innovations in Chemical Synthesis. Oxford, Butterworth-Heinemann, pp. 253-262.
Bongaerts, J.; Krämer, M.; Müller, U.; Raeven, L.; Wubbolts, M. (2001). Metabolic Engineering for Microbial Production of Aromatic Amino Acids and Derived Compounds. Metabolic Engineering, 3(4), pp. 289-300. https://dx.doi.org/10.1006/mben.2001.0196.
Doroshenko, V. G.; Livshits, V. A.; Airich, L. G.; Shmagina, I. S.; Savrasova, E. A.; Ovsienko, M. V.; Mashko, S. V. (2015). Metabolic Engineering of Escherichia coli for the Production of Phenylalanine and Related Compounds. Applied Biochemistry and Microbiology, 51(7), pp. 733-750. https://dx.doi.org/10.1134/s0003683815070017.
FINAR. (2019). Price List 2019-20, Gujarat, Finar Foundation,
García, J. M. (2008). La simulación de procesos en ingeniería química. Revista Investigación Científica, 4(2), pp. 1-9.
Gerigk, M.; Bujnicki, R.; Ganpo-Nkwenkwa, E.; Bongaerts, J.; Sprenger, G.; Takors, R. (2002). Process Control for Enhanced L-Phenylalanine Production Using Different Recombinant Escherichia coli Strains. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 80(7), pp. 746-754. https://dx.doi.org/10.1002/bit.10428.
Gerigk, M. R.; Maass, D.; Kreutzer, A.; Sprenger, G.; Bongaerts, J.; Wubbolts, M.; Takors, R. (2002). Enhanced pilot-scale fed-batch L-phenylalanine production with recombinant Escherichia coli by fully integrated reactive extraction. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng., 25, pp. 43–52. https://dx.doi.org/0.1007/s00449-002-0280-2.
Heinzle, E., Biwer, A. P., Cooney, C. L. (2006). Development of Sustainable Bioprocesses Modeling and Assessment. West Sussex, John Wiley & Sons, pp. 62-78.
Intelligen. (2018). SuperPro Designer® (Version 10.0). Scotch Plains, Intelligen, Inc.
Ito, H.; Sato, K.; Matsui, K.; Sano, K.; Enei, H.; Hirose, Y. (1990). Molecular breeding of a Brevibacterium lactofermentum L-phenylalanine producer using a cloned prephenate dehydratase gene. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 33, pp. 190-195. https://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF00176523.
Jenkins, S. (2020). Economic Indicators. Chemical Engineering, 127(2), pp. 56.
Klausner, A. (1985). Building for Success in Phenylalanine. Biotechnology, 3(4), pp. 301-307.
Lee, C. S.; Chong, M. F.; Binner, E.; Gomes, R.; Robinson, J. (2018). Techno-economic assessment of scale-up ofbio-flocculant extraction and production by usingokra as biomass feedstock. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 132, pp. 358–369. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2018.01.050.
Liu, C. H.; Liao, C. C. (1994). Medium optimization for L-phenylalanine production by a tryptophan auxotroph of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Biotechnol. Lett., 16, pp. 801-806.
Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ding, D.; Wen, J.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, D. (2018). Genetic engineering of Escherichia coli to improve L-phenylalanine production. BMC Biotechnology, 18(5), pp. 1-12. https://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12896-018-0418-1.
Mani, S.; Sundaram, J.; Das, K. C. (2016). Process simulation and modeling: Anaerobic digestion of complex organic matter. Biomass and Bioenergy, 93, pp. 158-167. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2016.07.018.
Matche. (2020). Chemical Equipment Cost. Disponible en www.matche.com. [Consultado 12 de abril 2020].
McEvoy, J. J.; Joyce, A. (1974). Production of L-phenylalanine by DL-phenylalanine hydroxamate-resistant Tyr- mutants of Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Cell. Biochem., 4(3), pp. 191-195. https://dx.doi.org/10.1007/bf01731480.
Meza, J. d. J. (2013). Evaluación financiera de proyectos, 3ra ed., Bogotá, D.C.: Ecoe Ediciones, pp. 133-199.
Miranda, R. d. C.; Mendes, M. F. (2018). Simulation of the Extractive Distillation of Ethanol-Water System: Evaluation of the Influence of Different Solvents. New Materials, Compounds and Applications, 2(2), pp. 152-167.
Molychem. (2019). Price List 2019-2021. Mumbai, Molychem.
Oxford. (2019). Price List 2020-2021 Maharashtra, Oxford Lab Fine Chem LLP.
Peters, M. S., Timmerhaus, K. D., West, R. E. (2003). Plant Design and Economics for Chemical Engineers, 5th ed., New York: McGraw-Hill, pp. 226-275.
Rüffer, N.; Heidersdorf, U.; Kretzers, I.; Sprenger, G. A.; Raeven, L.; Takors, R. (2004). Fully integrated L-phenylalanine separation and concentration using reactive-extraction with liquid-liquid centrifuges in a fed-batch process with E. coli. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng, 26, pp. 239–248. https://dx.doi.org/10.1007/ s00449-004-0354-4.
Sayar, N. A.; Pinar, O.; Kazan, D.; Sayar, A. A. (2019). Bioethanol Production From Turkish Hazelnut Husk Process Design and Economic Evaluation. Waste Biomass Valor, 10, pp. 909–923. https://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12649-017-0103-y.
Sigma-Aldrich. (2020). L-Phenylalanine PharmaGrade. Disponible en: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/sigma/p8740?lang=en®ion=CU. [Consultado 27 de abril 2020].
Sinnott, R., Towler, G. (2020). Chemical Engineering Design, 6th ed., Oxford, Butterworth-Heinemann, pp. 275-361.
Sprenger, G. A. (2007). From scratch to value: engineering Escherichia coli wild type cells to the production of L-phenylalanine and other fine chemicals derived from chorismate. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 75(4), pp. 739–749. https://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-0931-y.
Sun, Z.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, C. (2016). Separation and purification of L-phenylalanine from the fermentation broth by electrodialysis. Desalination and Water Treatment, 57(47), pp. 1-7. https://dx.doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015. 1137082.
Towler, G., Sinnott, R. (2013). Chemical Engineering Design. Principles, Practice and Economics of Plant and Process Design, 2nd ed., Oxford, Butterworth-Heinemann, pp. 389-425.
Vučurović, D. G.; Dodić, S. N.; Popov, S. D.; Dodić, J. M.; Grahovac, J. A. (2012). Process model and economic analysis of ethanol production from sugar beet raw juice as part of the cleaner production concept. Bioresource Technology, 104, pp. 367–372. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.10.085.
Wu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Sun, J.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, D. (2019). Application of Dynamic Regulation to Increase L-Phenylalanine Production in Escherichia coli. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 29(6), pp. 923–932. https://dx.doi.org/10.4014/ jmb.1901.01058.
WVU. (2020) Batch Production of Aminoacids. Disponible en: https://cbe.statler.wvu.edu/files/d/450550ca-9cab-4688-a9b8-f73bc1c72707/ batch-production_of_ amino_acids.pdf. [Consultado 5 de febrero de 2020].
Yuan, P.; Cao, W.; Wang, Z.; Chen, K.; Li, Y.; Ouyang, P. (2015). Enhancement of L-phenylalanine production by engineered Escherichia coli using phased exponential L-tyrosine feeding combined with nitrogen source optimization. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 120(1), pp. 36-40. https://dx.doi.org /10.1016/j.jbiosc.2014.12.002

 PDF
PDF
 FLIP
FLIP